Why Do You Need to Model
Inappropriate progression is often seen on a stage of the soft launch. We may observe that a player passes through the game too fast and content is exhausted after several days of playing. It could be that the player reaches high levels in the first two hours of playing and continues leveling up quickly.
These are consequences of too fast progression, which leads to a surplus of in-game currency and the player finishes the game too fast. This is bad for the in-app monetization because in-game resources are gradually accumulating with progression. It also limits ad monetization because a player stays in the game not as long as he could.
The opposite situation, when a player is passing the level too long, gets bored or frustrated which leads to a high churn rate.
Appropriate in-game metrics observation and analysis reveal these problems on the soft launch, but statistical simulations allow to fine-tune progression much earlier, on a stage of game design. This will help to avoid altogether or at least reduce progression-based problems and save time during the soft launch.
Below we are going to show an example of progression fitting by user’s behavior simulations for a case of a simple trivia game. The goal of the article is to show a general approach to the progression curve fitting based on simulations that can be undertaken on a stage of the economy design prior to launch.

Example of Trivia Game Modeling Progression
For example, let’s take the following trivia game:
A game consists of rounds with a set of 10 questions, each question has 4 variants of answers. If the answer is correct, a player receives an XP reward and passes to the next questions. Giving the wrong answer, they should re-start the round from the 1st question. When answering all questions in a round correctly, a player receives a bonus and a higher XP reward. They also receive rewards when leveling up.
So, two sources are present: correct answer on the last question and a level up. We have to design a progression through the game to make these 2 sources occur reasonably often. This task consists of two subtasks:
Define a number of questions in a round. Should it be 10, or maybe 5, or 20? Then we should find how often a player will complete a round and get a reward.
We need to fit xp-to-level formula, making level progression faster at the beginning and slower later. Then we could make a rough estimation of how often level-ups will occur.
Fitting Progression 1. Defining The Quantity Of Questions Per Round
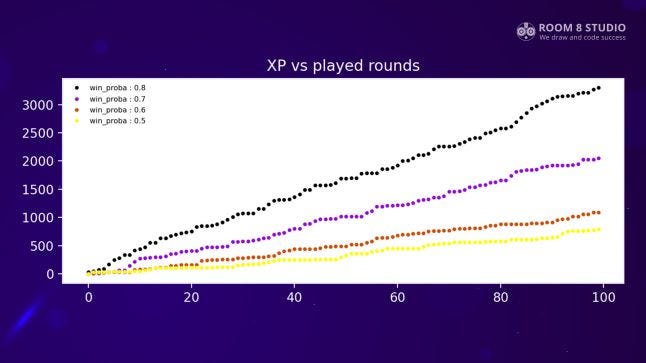
Let’s characterize the player’s behavior by the probability of giving a correct answer. Guessing randomly on 4 variants of answer, a probability of being correct is 0.25. We expect that players will play better than random guessing, at least those who like our game and stays there. If there is a competition with another real player, we may expect the probability to win as 0.5. In fact, such player most probably will leave our game. But we can take it as a lower-bound estimation. As an upper-bound estimation, we’ll set 0.9, meaning that player answers on 9 questions from 10 correctly. Actually, this means that questions are too easy and should be re-designed. So let’s take players with probabilities of winning as 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9 to see the broad range of behavior. Here 0.6-0.8 are expected probabilities, 0.5 and 0.9 - are edge cases.
Let’s sample from a binomial distribution a sequence of events with lengths 5, 7, 10, 15, corresponding to the number of questions in a round and pass winning probabilities as a parameter of the distribution. Repeat this 1000 times and calculate average (1) attempt at which a player reaches the last question, (2) length of the round.
attempts to reach last q-n
win proba | # of questions | mean | median | mean | median |
5 | 0.90.80.70.60.5 | 1411141933 | 810101323 | 3.52.71.91.41 | 52.5111 |
7 | 0.90.80.70.60.5 | 19192750122 | 1413193787 | 4.83.12.11.41 | 63111 |
10 | 0.90.80.70.60.5 | 2736802581025 | 192559182703 | 5.83.62.21.41 | 63111 |
15 | 0.90.80.70.60.5 | 43116481319132475 | 2984338225524017 | 6.842.31.51 | 63111 |
20 | 0.90.80.70.60.5 | 75369292042610 | 53260191830506 | 8.23.92.31.51.4 | 73111 |
As seen in Table 1, in the case of 10 questions in a round, a not very good player with winning probabilities of 0.5 - 0.6 needs to make around 200 or more attempts to reach the last question and get a bonus. In a case of 5 questions, a relatively good player with winning probabilities 0.8-0.9 is reaching last question in around 10 attempts, which looks too often. Approximately 7 questions per round look more reasonable, but a bit fast too. In cases of 7 and 10 questions per round, an average length of a round is 1-3 questions for probabilities 0.6 - 0.8.
A good choice will be to take 9 or 8 questions per round and design the first one or two questions very easily. Then a player will reach the last question in about 30-60 attempts while the average duration of a round would be 2 - 4 (or 3 - 6) questions per round. Later, if deciding to put some limitations on the number of sessions per day or balancing currencies we should take into account these values.
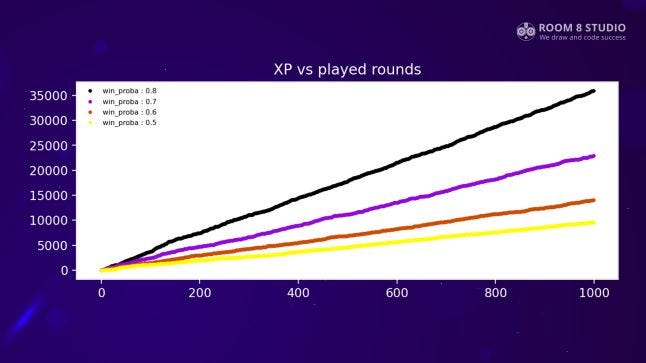
Fitting progression 2: XP vs Played Rounds
The second step is to design an XP-to-level formula. If we are planning rewards on level up, we should make an estimation of how often they occur at the beginning of a game and later. At the beginning of a game level ups should happen often for better engagement, but then it should slow down, otherwise, there would be a continuous surplus of resources.