,
,Over 1.2 million internet-connected healthcare devices and systems that expose patient data have been identified in research by Modat. The United States, South Africa, and Australia topped the list, with vulnerable systems including MRI scanners, CT machines, and hospital management platforms.
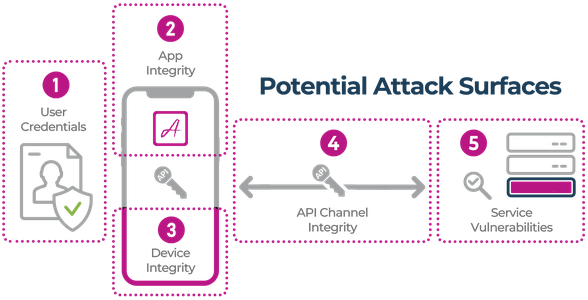
Using its Modat Magnify platform, the company identified misconfigurations, weak passwords, and unpatched software as common risks. Some devices had no authentication, while others used factory-default passwords such as 'admin' or '123456'. Sensitive MRI, dental X-ray, and blood test records were accessed.
Modat worked with Health-ISAC and Dutch CERT Z-CERT for responsible disclosure, alerting organisations to secure exposed systems. CEO Soufian El Yadmani said devices should never be open to the internet without safeguards, warning that remote access must be secure.
The research stressed that healthcare cybersecurity is a patient safety issue. Outdated or unprotected devices could enable fraud, extortion, or network breaches. Regular security checks, asset inventories, and monitoring were recommended to reduce risks.
Founded in 2024, Modat uses its Device DNA dataset to catalogue internet-connected devices globally. It aims to help healthcare and other sectors close the gap between rising cyber threats and effective resilience.