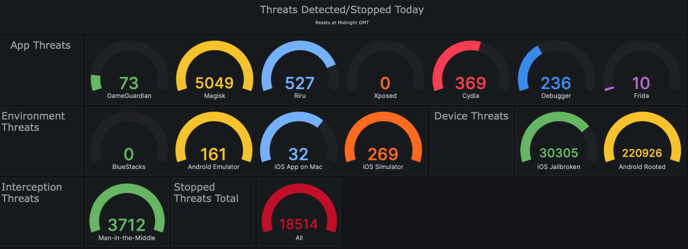
Here is a list of 20 common threats that impact mobile app security and API security:
-
Data Breaches:
Unauthorized access leading to the exposure of sensitive user data. Risks include personal information (PII), credentials, and financial data. -
Man-in-the-Middle Attacks (MitM):
Interception of communication between mobile apps and APIs, allowing attackers to eavesdrop or modify data. -
Code Tampering:
Unauthorized modification of the mobile app's code, potentially leading to functionality alterations or the injection of malicious code. -
Reverse Engineering:
Extraction of source code or sensitive information from the mobile app, often for the purpose of creating counterfeit versions. -
API Security Risks:
Inadequate protection of APIs, leading to vulnerabilities such as unauthorized access, injection attacks, and data exposure. -
Credential Theft:
Unauthorized acquisition of user credentials, often through phishing attacks or exploitation of weak authentication mechanisms.
-
Device Compromise:
Compromised mobile devices can expose sensitive information and compromise the security of mobile apps. -
Malicious App Installations:
Installation of counterfeit or malicious apps that imitate legitimate ones, potentially leading to data theft or unauthorized access. -
Insecure Data Storage:
Weak encryption or improper storage of sensitive data on the device, making it vulnerable to unauthorized access. -
Insufficient Transport Layer Protection:
Lack of proper TLS encryption during data transmission, exposing information to interception and manipulation. -
Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks:
Overwhelming a mobile app or API with traffic to disrupt its availability, causing service downtime. -
Phishing Attacks:
Deceptive techniques to trick users into revealing sensitive information, such as login credentials or personal details. -
Mobile Malware:
Malicious software specifically designed to exploit vulnerabilities in mobile devices or apps, leading to unauthorized access or data theft. -
Lack of Binary Protections:
Absence of safeguards against reverse engineering or code analysis, allowing attackers to gain insights into the app's inner workings. -
Weak Session Management:
Inadequate controls over user sessions, leading to vulnerabilities like session hijacking or session fixation. -
Non-compliance with Security Standards:
Failure to adhere to established security standards and best practices, exposing apps and APIs to known vulnerabilities. -
Unsecured Third-Party Libraries:
Integration of insecure or outdated third-party libraries, introducing potential vulnerabilities into the mobile app. -
Poorly Implemented Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
Inadequate implementation of MFA, allowing attackers to bypass additional authentication measures. -
Inadequate Security Awareness:
Lack of awareness among users and developers about potential security threats and best practices. -
Supply Chain Attacks:
Compromising the security of a mobile app or API through vulnerabilities in its supply chain, including third-party services or components.