Game applications rely primarily on devices to obtain location information, which creates ample opportunities for fraud within the Game Black/Gray Industry. Across different mobile operating systems, the methods for implementing virtual location spoofing are highly diverse.
Three Methods for Implementing Virtual Location on iOS:
■ Using Xcode, edit the GPX file to invoke the com.apple.dt.simulatelocation service on the device and write latitude and longitude coordinates.
■ Achieve virtual location tracking by sending simulated location data through hardware peripherals.
■ On jailbroken devices, implement virtual location tracking by hooking the location delegate methods within CLLocationManager.
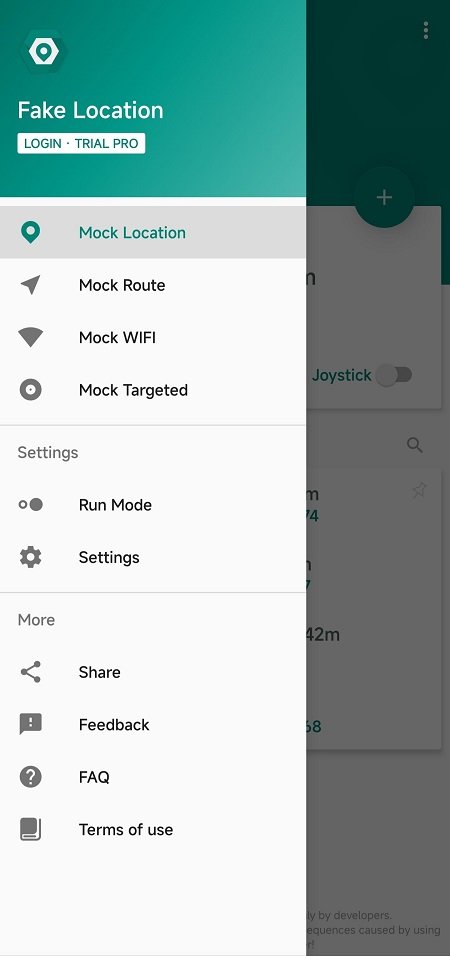
On Android devices, due to their open-source nature, the system inherently grants developer permissions. Starting from Android 6.0 and above, users can enable location access for apps by navigating to Developer Options → Select mock location app. This allows for virtual positioning through methods such as tampering with API interface data, injecting fake location information, or forging GPS positioning data.
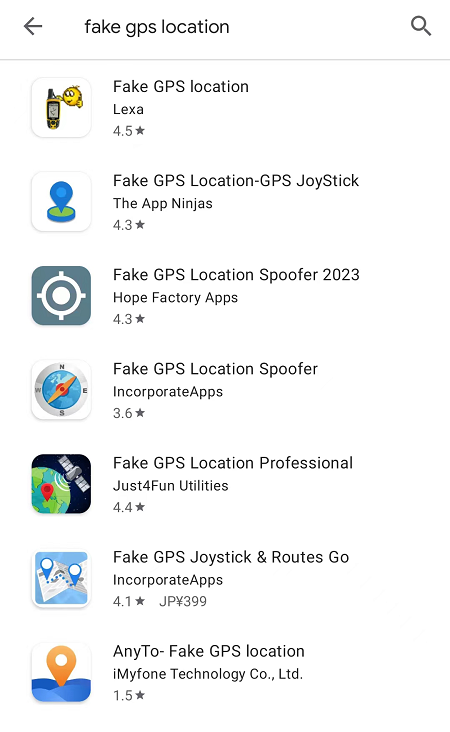
Tampering with virtual location data severely impacts location-based service (LBS) games. Since the core gameplay relies on the positioning system, allowing players to manipulate in-game resources by constantly altering their physical location directly undermines the fairness of the game's fundamental mechanics.

To address the virtual location risks faced by games, JikGuard has developed a mature and comprehensive protection solution. It has been integrated into multiple popular games and has demonstrated outstanding protection capabilities.
Prevent Geolocation Tampering
Disable geolocation spoofing operations to prevent cheating in location-based service (LBS) game mechanics.
Anti-Injection Features
Prohibits the use of third-party injection tools such as Xposed and Frida, preventing malicious activities like modifying game memory after injection. Any detected attempts will result in immediate force closure.








